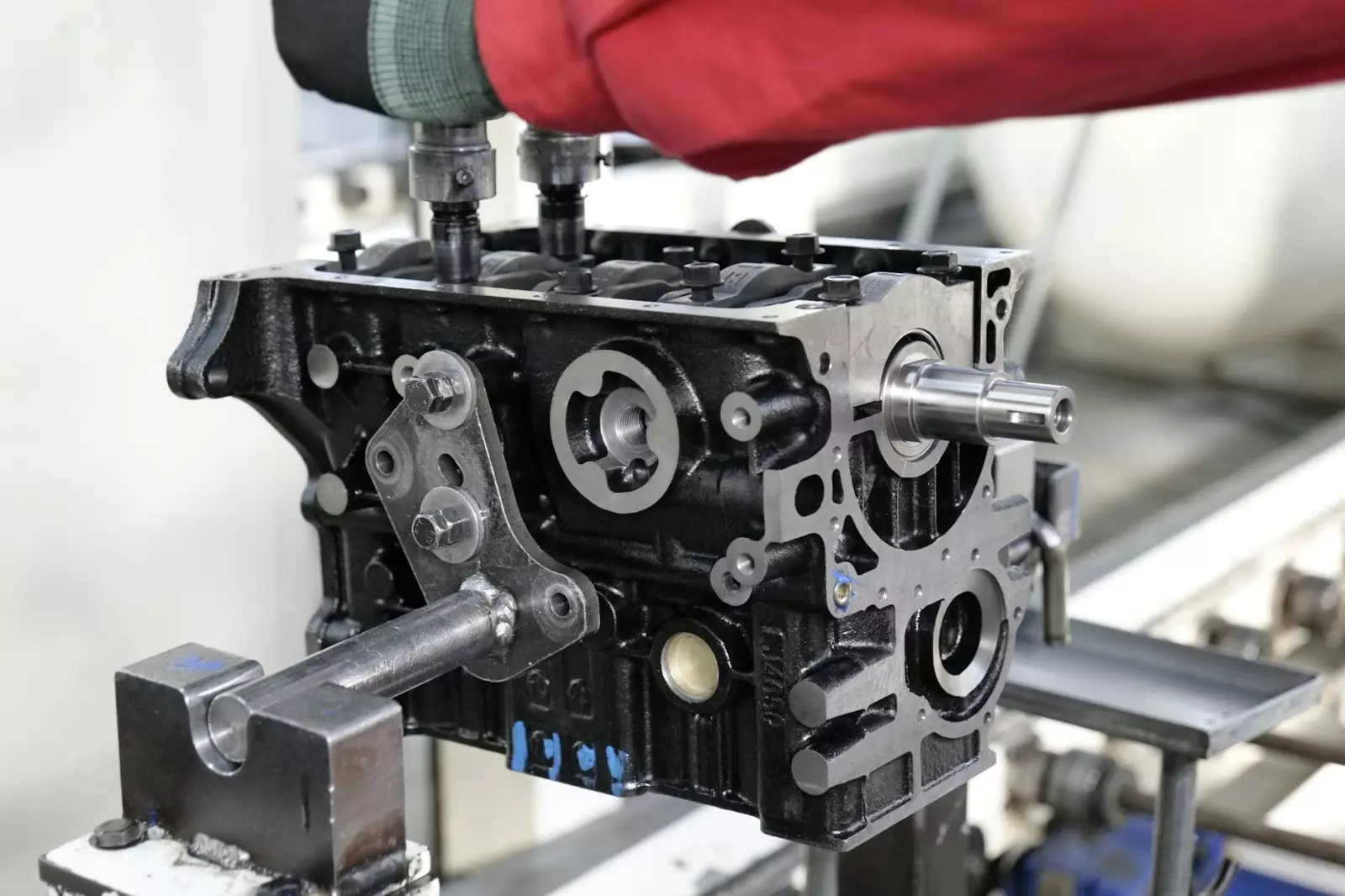
The internal combustion engine, an intricate assembly of components, is the heart of most vehicles on the road today. Each part plays a critical role in ensuring smooth operation and performance. Over the years, I have encountered a range of problems that often arise within these systems, with certain components displaying a tendency to fail under specific conditions. Understanding these tendencies not only aids in diagnostics but also in preventing future issues.
One of the most critical components is the engine block itself, which serves as the foundation for the entire engine assembly. Typically made of cast iron or aluminum, the block houses the cylinders and provides the necessary structure for mounting other components. Over time, thermal expansion and contraction can lead to hairline cracks, particularly in high-performance applications or in engines subjected to extreme operating conditions. These cracks may not always present immediate symptoms but can lead to coolant leaks, oil contamination, or even catastrophic failure if left unchecked.
The cylinder head, responsible for sealing the combustion chamber and housing components such as valves and spark plugs, is another area where problems frequently arise. Warping is a common issue, often exacerbated by overheating. In many cases, drivers may notice a loss of power or misfires before any visible signs appear. When a head gasket fails due to excessive heat or pressure, the consequences can be severe, leading to engine overheating and significant damage. Regular monitoring of coolant levels and engine temperature can help mitigate risks associated with these failures.
Valvetrain Components and Their Vulnerabilities
The valvetrain, which includes components such as camshafts, lifters, and pushrods, is essential for managing the timing of air and fuel intake as well as exhaust expulsion. In high-mileage engines, wear and tear on these parts can lead to a range of issues. For instance, hydraulic lifters can become clogged with sludge or debris, resulting in noisy operation or loss of lift. Similarly, worn camshaft lobes can lead to uneven valve operation, which can affect engine performance.
In my experience, the symptoms of valvetrain wear often manifest as a ticking noise, particularly noticeable at idle. This sound may be dismissed as normal engine noise, but it often indicates deeper issues that, if ignored, could lead to more serious engine damage. Regular oil changes and using high-quality oil can help reduce the buildup of sludge, thereby prolonging the life of these components.
Fuel System Failures
Fuel delivery is another critical aspect of engine performance. Fuel injectors, pumps, and filters are all susceptible to failure, especially in vehicles that use low-quality fuel or have not had routine maintenance. Clogged fuel filters can restrict flow, leading to poor engine performance and stalling. Similarly, fuel pumps can fail due to wear or overheating. In many instances, drivers may experience symptoms such as difficulty starting, misfiring, or decreased acceleration, which can be attributed to these components.
In the field, I have often observed that fuel injectors can become clogged or damaged, leading to uneven fuel distribution among cylinders. This results in poor combustion efficiency and can cause engine knocking or pinging. Cleaning or replacing fuel injectors is sometimes necessary to restore optimal performance, and I’ve found that using fuel additives can help maintain cleaner injectors over time.
Cooling System Considerations
The cooling system plays a vital role in regulating engine temperature and preventing overheating. Components such as the radiator, water pump, and thermostat are crucial. A malfunctioning thermostat can cause the engine to run either too hot or too cold, leading to decreased efficiency and increased emissions. In many cases, drivers may notice fluctuating temperature gauges or, in severe cases, steam rising from the engine bay.
Water pumps, which circulate coolant throughout the engine, are prone to failure due to wear on bearings or seals. A failed water pump can result in rapid overheating and engine damage. In practice, a consistent observation is the presence of coolant leaks, often indicating a failing pump. Regular inspection of coolant levels and system pressure can help identify potential issues before they escalate.
Lubrication System Challenges
The lubrication system is essential for minimizing friction and wear on engine components. Oil pumps, filters, and the oil itself must all be in good condition to ensure proper operation. In many cases, I have seen oil filters become clogged, leading to reduced oil flow and increased wear on engine parts. This issue is often exacerbated by extended oil change intervals, which can lead to the breakdown of oil quality.
Engine oil plays a crucial role in protecting components from wear and heat. Using the wrong viscosity oil can lead to inadequate lubrication, especially in high-stress environments. In my experience, engines that are run with incorrect oil viscosity often exhibit increased wear on bearings and camshafts. It’s essential to adhere to manufacturer specifications regarding oil type and change intervals to maintain optimal engine health.
Electrical System Failures
The electrical system, while not a mechanical component per se, is integral to engine operation. Sensors, wiring, and the engine control unit (ECU) all work together to optimize performance. Failures in this system can lead to a range of issues, from poor fuel economy to complete engine shutdown. I have frequently encountered faulty sensors, such as oxygen or mass airflow sensors, which can cause the ECU to miscalculate fuel delivery, leading to rough idling or stalling.
Wiring harnesses are also susceptible to wear and damage due to heat and vibration. In some cases, corroded connectors can lead to intermittent issues that are difficult to diagnose. Regular inspection of electrical connections and harnesses can help identify potential problems before they affect engine performance.
In summary, the complexities of engine components necessitate a thorough understanding of their functions and common points of failure. While some issues may appear minor initially, they can escalate into significant problems if not addressed promptly. Routine maintenance, attention to operating conditions, and an awareness of the unique vulnerabilities of each component can help mitigate these risks. In my experience, being proactive rather than reactive often saves time and resources in the long run.